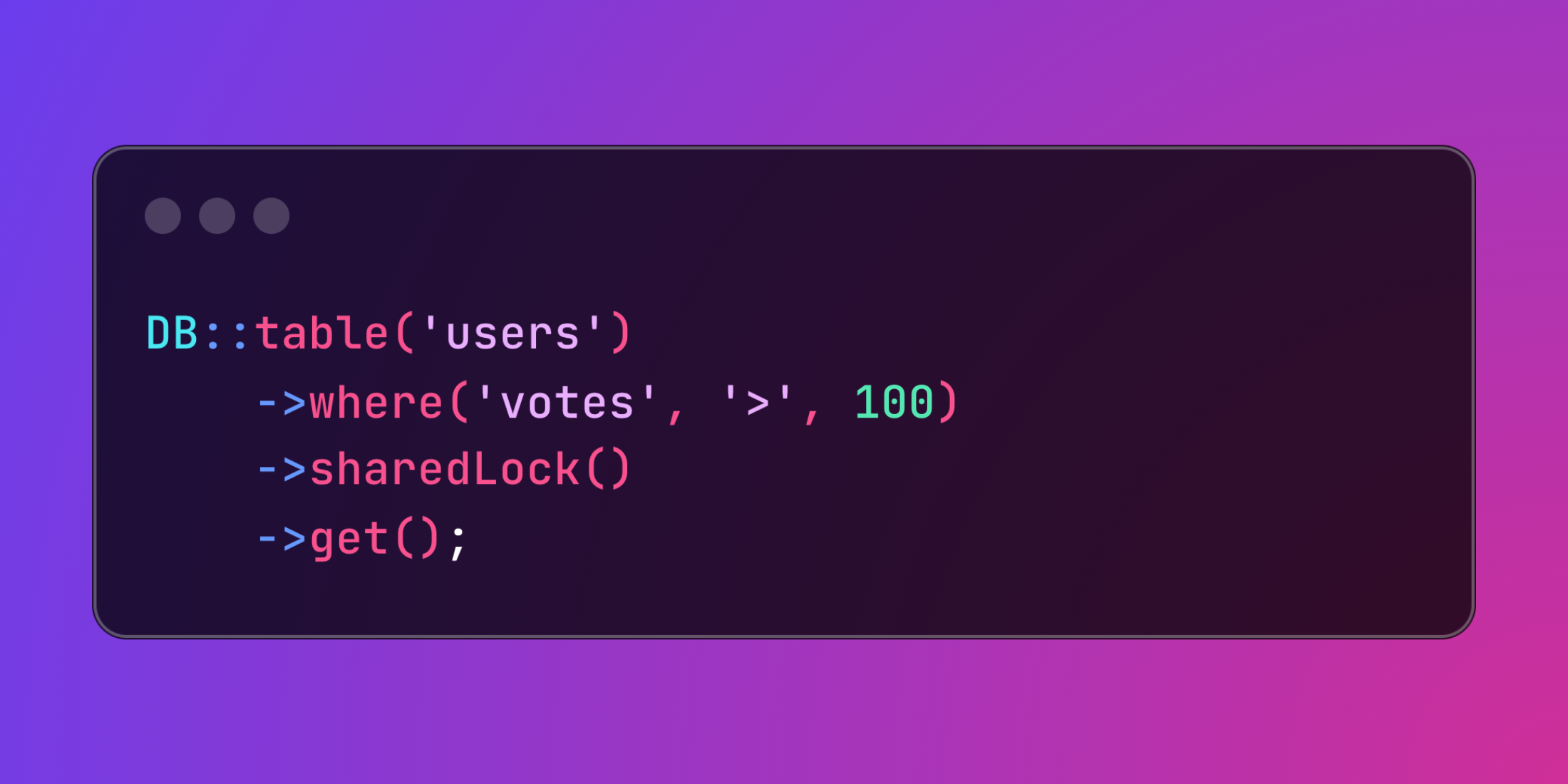
Laravel provides robust pessimistic locking capabilities to prevent data races in concurrent database operations. Through sharedLock() and lockForUpdate() methods, you can maintain data consistency in high-concurrency scenarios.
The sharedLock() method prevents modifications while allowing reads:
DB::table('users') ->where('votes', '>', 100) ->sharedLock() ->get();For more stringent control, lockForUpdate() blocks both modifications and shared locks:
DB::table('orders') ->where('status', 'pending') ->lockForUpdate() ->get();This approach is particularly valuable in financial transactions or inventory management systems:
class PaymentController extends Controller{ public function processPayment($orderId, $amount) { return DB::transaction(function () use ($orderId, $amount) { $account = DB::table('accounts') ->where('order_id', $orderId) ->lockForUpdate() ->first(); if ($account->balance >= $amount) { DB::table('accounts') ->where('order_id', $orderId) ->update(['balance' => $account->balance - $amount]); return ['success' => true, 'message' => 'Payment processed']; } return ['success' => false, 'message' => 'Insufficient funds']; }); }}These locking mechanisms are essential in applications where data accuracy is crucial and multiple processes might attempt to modify the same data simultaneously.