Implement Conditional Migrations in Laravel with the New shouldRun() Method
Last updated on by Harris Raftopoulos
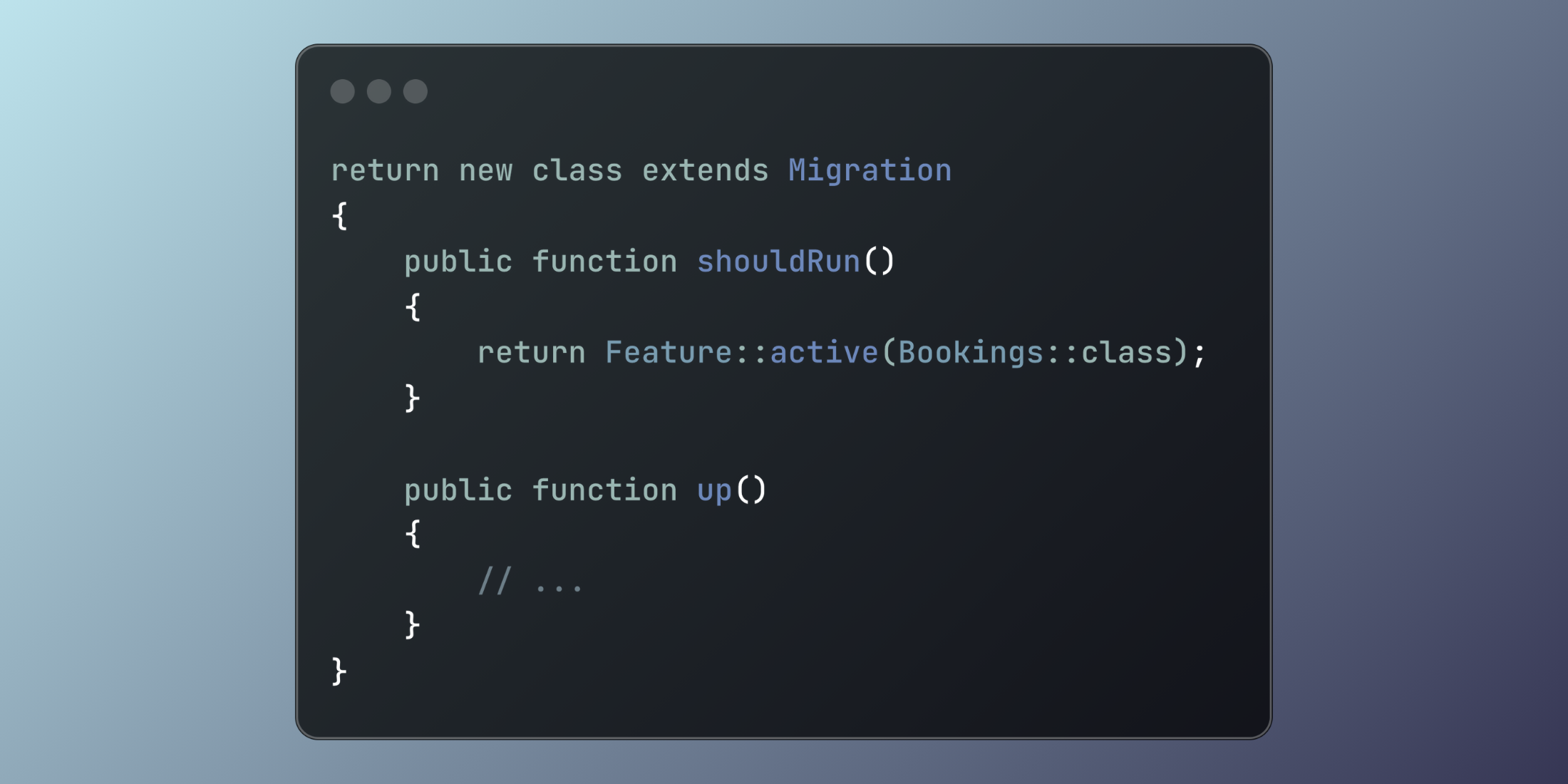
Laravel solves the challenge of managing migrations with feature flags through the new shouldRun() method. This elegant addition allows migrations to execute conditionally based on application state, simplifying phased rollouts and feature management.
When implementing feature flags or staged deployments, certain database changes should only apply when specific features are active. Previously, developers relied on complex workarounds or manual migration tracking. The shouldRun() method provides a clean solution by allowing migrations to determine their own execution criteria:
return new class extends Migration{ public function shouldRun() { return Feature::active(Bookings::class); } public function up() { Schema::create('bookings', function (Blueprint $table) { $table->id(); $table->string('location'); $table->timestamps(); }); } public function down() { Schema::dropIfExists('bookings'); }}This migration executes only when the 'Bookings' feature is active. When inactive, the migration gets skipped without errors, and no entry appears in the migrations table.
The method proves particularly valuable for multi-tenant applications or gradual feature rollouts:
// 2023_06_22_create_notification_tables.phpreturn new class extends Migration{ public function shouldRun() { // Only run this migration for environments or tenants // with the notification system enabled return config('features.advanced_notifications') === true; } public function up() { Schema::create('notification_templates', function (Blueprint $table) { $table->id(); $table->string('channel'); $table->json('content'); $table->timestamps(); }); Schema::create('notification_delivery', function (Blueprint $table) { $table->id(); $table->string('recipient'); $table->json('metadata'); $table->timestamps(); }); } public function down() { Schema::dropIfExists('notification_delivery'); Schema::dropIfExists('notification_templates'); }};The shouldRun() method works consistently with both migrate and rollback commands. Migrations skipped during migration will also be skipped during rollback operations, maintaining database integrity.
By implementing the shouldRun() method, developers create more adaptable, context-aware migrations that respond to application requirements, making feature management and progressive deployment strategies more effective and manageable.
















