What you'll learn
- Understand BSON and MongoDB's document structure.
- Perform basic CRUD operations on documents.
- Choose between embedding and referencing.
- Model one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many relationships effectively.
You will need basic Laravel knowledge.
BSON & document structure
What is BSON?
Binary JSON (BSON) is MongoDB’s binary-encoded representation of JSON-like documents. It includes explicit type and length information, enabling fast traversal and efficient storage compared to plain JSON.
In practice, BSON is the format used on disk and over the wire, while you typically read and write JSON-like structures in code.
Basically, BSON is the secret sauce behind MongoDB’s success.
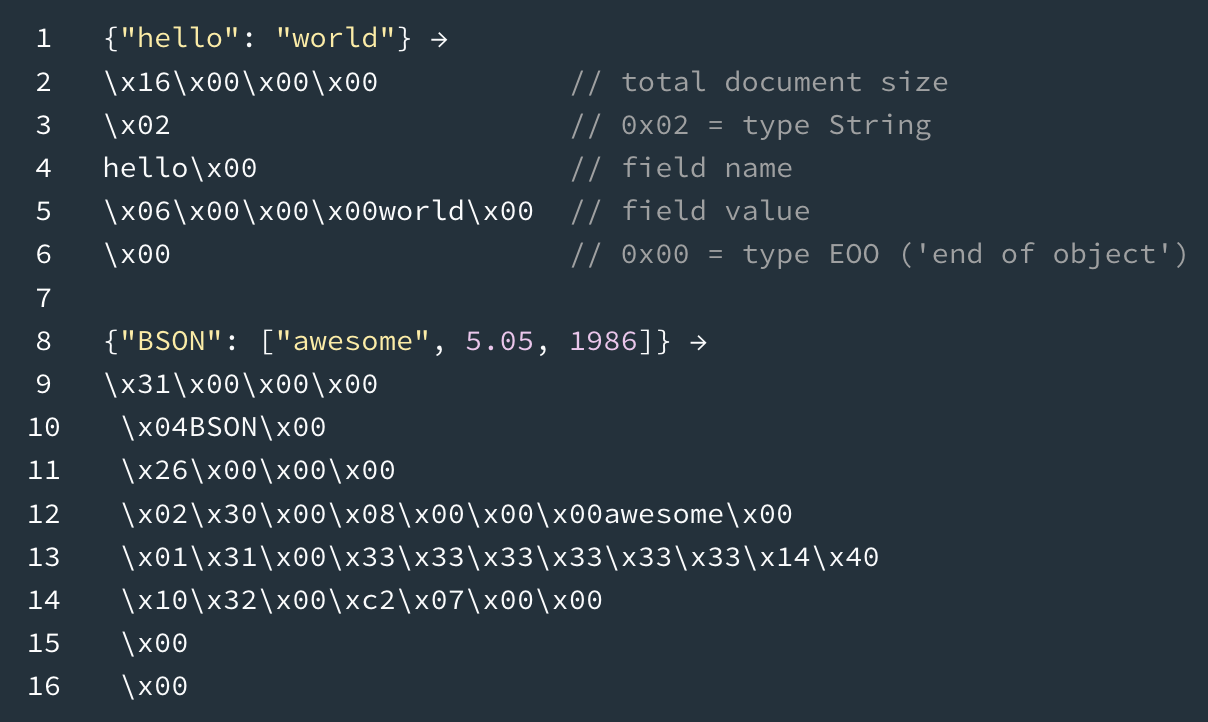 Example of how BSON looks like
Example of how BSON looks like
BSON data types
BSON extends JSON with additional data types like date, ObjectId, and binary data.
| Data Type | Description | Example ||-----------|-------------|---------|| String | UTF-8 string | `"John Doe"` || Integer | 32-bit or 64-bit integer | `28` || Double | 64-bit floating point | `3.14` || Boolean | true/false | `true` || Date | UTC datetime | `ISODate("2025-01-15")` || ObjectId | 12-byte unique identifier | `ObjectId("507f...")` || Array | List of values | `["tag1", "tag2"]` || Object | Embedded document | `{"city": "NY"}` || Null | Null value | `null` |Document anatomy
A sample of how a BSON document looks like with the shown data schema provided above.
{ "_id": ObjectId("507f1f77bcf86cd799439011"), "name": "John Doe", "email": "john@example.com", "age": 28, "created_at": ISODate("2025-01-15T10:30:00Z"), "profile": { "bio": "Software developer", "avatar": "avatar.jpg" }, "tags": ["developer", "laravel", "mongodb"]}What is a collection?
A collection is a group of documents. Unlike SQL tables, documents in the same collection do not need to share an identical schema.
 To understand the MongoDB terminologies in comparison to SQL database:
To understand the MongoDB terminologies in comparison to SQL database:
| MongoDB | SQL |
|---|---|
| Collection | Table |
| Document | Row |
| Field | Column |
Data modeling fundamentals
MongoDB offers two primary patterns for relating data: embedding and referencing.
Embed
Embedding stores related data inside the same document.
Guiding rule: Data accessed together should be stored together.
Example—profile information embedded in a user document:
{ "_id": ObjectId("507f1f77bcf86cd799439011"), "username": "john.doe123", "email": "john@example.com", "profile": { "full_name": "John Doe", "bio": "Software developer and tech enthusiast", "avatar": "https://api.dicebear.com/7.x/avataaars/svg?seed=123e4567", "website": "https://example.com", "location": "San Francisco, USA" }}// app/Models/User.php// These examples use Laravel's database factories with Faker for generating test data....'profile' => [ 'full_name' => $firstName . ' ' . $lastName, 'bio' => fake()->sentence(10), 'avatar' => 'https://api.dicebear.com/7.x/avataaars/svg?seed=' . fake()->uuid(), 'website' => fake()->url(), 'location' => fake()->city() . ', ' . fake()->country(),],... // app/Models/UserController.php...
public function updateProfile(Request $request){ $validated = $request->validate([ 'full_name' => 'sometimes|string|max:100', 'bio' => 'sometimes|string|max:500', 'website' => 'sometimes|url', 'location' => 'sometimes|string|max:100', ]); $user = auth()->user(); $user->update([ 'profile' => array_merge($user->profile, $validated), ]);}Another embed—frequently displayed user stats:
{ "_id": ObjectId("507f1f77bcf86cd799439012"), "username": "jane.smith456", "stats": { "posts_count": 42, "followers_count": 1250, "following_count": 87 }}// app/Models/User.php...'stats' => [ 'posts_count' => 0, 'followers_count' => 0, 'following_count' => 0,],...Pros
- Single query to retrieve cohesive data
- Single atomic update for the whole unit
Cons
- Large documents risk hitting the 16 MB limit. (Large arrays or embedded documents can hit this limit.)
- There is possible duplication when the same subdata appears elsewhere.
Reference
Referencing links documents across collections using their IDs. This mirrors foreign keys in relational databases.
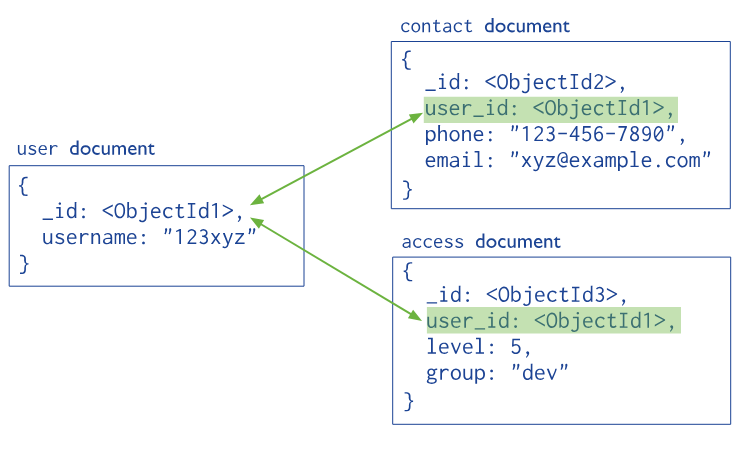 Referencing User in Contact and Access
Referencing User in Contact and Access
Example: Posts reference users. Posts are unbounded and grow continuously, so referencing keeps user documents small and posts independent.
{ "_id": ObjectId("507f1f77bcf86cd799439013"), "user_id": ObjectId("507f1f77bcf86cd799439011"), "content": "My awesome post!", "stats": { "likes_count": 342, "comments_count": 28 }}// app/Models/Post.php
// Model definitionprotected $fillable = [ 'user_id', // Reference to User 'content', 'media', 'stats', 'tags',]; // Relationshippublic function user(){ return $this->belongsTo(User::class, 'user_id');}// UserController.php...
public function show(User $user){ $user->load(['posts' => function($q) { $q->orderBy('created_at', 'desc')->limit(10); }]); $isFollowing = in_array( $user->_id, auth()->user()->following_ids ?? [] ); return view('users.show', compact('user', 'isFollowing'));}Comments reference both post and user:
{ "_id": ObjectId("507f1f77bcf86cd799439014"), "post_id": ObjectId("507f1f77bcf86cd799439013"), "user_id": ObjectId("507f1f77bcf86cd799439012"), "parent_id": null, "content": "Great post! I totally agree.", "likes_count": 15, "created_at": ISODate("2024-11-03T10:30:00Z"), "updated_at": ISODate("2024-11-03T10:30:00Z")}// app/Models/Post.php// Model definitionprotected $fillable = [ 'post_id', // Reference to Post 'user_id', // Reference to User 'parent_id', // Reference to parent Comment 'content', 'likes_count', 'created_at', 'updated_at',]; // Relationshipspublic function post(){ return $this->belongsTo(Post::class, 'post_id');} public function user(){ return $this->belongsTo(User::class, 'user_id');}All in all, referencing is commonly used in many-to-many relationships.
Pros
- Avoids duplication across collections
- Keeps hot documents small; supports independent querying
Cons
- Requires multiple queries or $lookup joins for aggregates
Model relationships
One-to-one
If data is always accessed together, embed.
// app/Models/Post.php'stats' => [ 'likes_count' => fake()->numberBetween(0, 1000), 'comments_count' => fake()->numberBetween(0, 50), 'shares_count' => fake()->numberBetween(0, 20),], // Sample Document{ "_id": ObjectId("507f1f77bcf86cd799439013"), "content": "My awesome post!", "stats": { "likes_count": 342, "comments_count": 28, "shares_count": 5 }}One-to-many cardinality
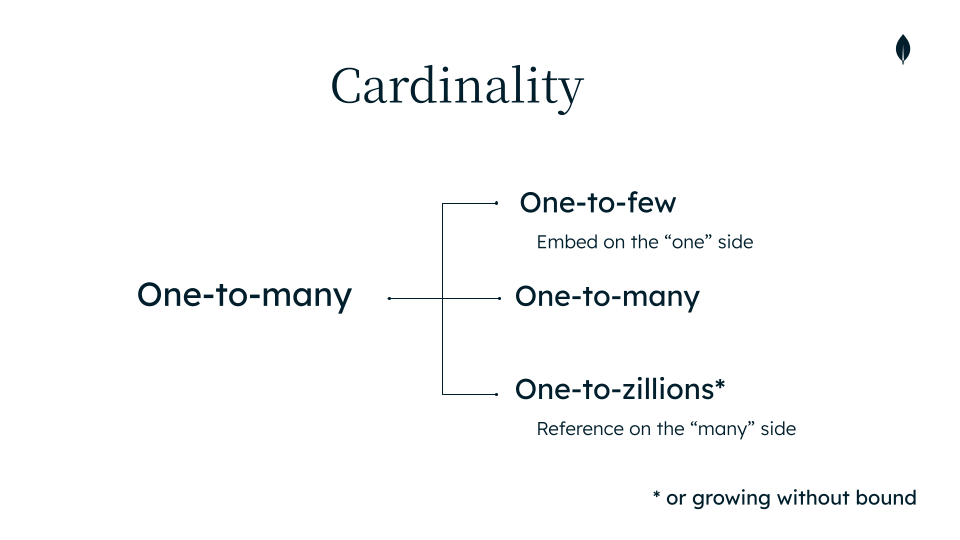 One-to-many cardinality variants
One-to-many cardinality variants
- One-to-few: small, bounded sets; prefer embed
{ "media": [ { "type": "image", "url": "..." }, { "type": "image", "url": "..." }, { "type": "video", "url": "..." } ]...}- One-to-many (bounded): Embed if items are limited and fetched with parent; example: replies limited to 50 per comment.
Comment::where('parent_id', $commentId)->get()- One-to-many (unbounded): Reference if items grow without limit or are queried independently; example: comments on posts.
// User.phppublic function comments(){ return $this->hasMany(Comment::class, 'user_id');} // Comment.phppublic function user(){ return $this->belongsTo(User::class, 'user_id');}- One-to-zillions: When a relationship can grow to thousands or millions, always reference from the "many" side to the "one" side; example: likes on a viral post.
{ "_id": ObjectId("507f1f77bcf86cd799439015"), "user_id": ObjectId("507f1f77bcf86cd799439012"), "likeable_type": "App\\Models\\Post", "likeable_id": ObjectId("507f1f77bcf86cd799439013")}// Query for likes: Paginated likes on a postLike::where('likeable_type', Post::class) ->where('likeable_id', $postId) ->paginate(20);Many-to-many
This is typically solved with referencing; example: following relationships.
class User extends Model{ protected $connection = 'mongodb'; protected $fillable = ['name', 'email', 'following_ids']; protected $casts = [ 'following_ids' => 'array' ];} // Follow a user$user->push('following_ids', $targetUserId); // Unfollow$user->pull('following_ids', $targetUserId); // Get following users$following = User::whereIn('_id', $user->following_ids)->get();Note: Many-to-many can also be modeled with a dedicated join collection if you need metadata on the edge, such as timestamps or statuses.
Additional example (outside the case study):
Products ↔ Tags with a join collection
When you need metadata on the relationship itself, create a dedicated join collection.
- Collections: products, tags, product_tags
- Edge metadata: who added the tag, when, and an optional relevance score
// products{ _id: ObjectId("6560..."), name: "UltraSoft Hoodie", sku: "HD-001" } // tags{ _id: ObjectId("6561..."), name: "winter" }{ _id: ObjectId("6562..."), name: "sale" } // product_tags (join collection){ _id: ObjectId("6570..."), product_id: ObjectId("6560..."), tag_id: ObjectId("6561..."), added_by: ObjectId("user123..."), added_at: ISODate("2025-10-15T09:12:00Z"), relevance: 0.87} // app/Models/ProductTag.phpclass ProductTag extends Model{ protected $connection = 'mongodb'; protected $fillable = ['product_id', 'tag_id', 'added_by', 'added_at', 'relevance']; protected $casts = [ 'added_at' => 'datetime', 'relevance' => 'float', ];} // Attaching a tag with metadataProductTag::create([ 'product_id' => $productId, 'tag_id' => $tagId, 'added_by' => auth()->id(), 'added_at' => now(), 'relevance' => 0.87,]);This pattern generalizes to other domains like:
- students ↔ courses (with grade and semester).
- users ↔ organizations (with role and since).
- authors ↔ publications (with order and contribution percentage).
Embed vs reference
| Factor | Embed | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Potential growth | Few items | Unlimited |
| Access pattern | Together | Independent |
| Document size | Stay small | Grow large |
| Update frequency | Rare | Frequent |
Conclusion
Choosing between embedding and referencing depends on cardinality, growth, access patterns, and update frequency.
Start with how your application reads data. If data is always fetched together and bounded, embed. If growth is unbounded or items are queried independently, reference.
Model to your workload, validate with real queries, and iterate as your app evolves.
Additional resources
- MongoDB Document Relationships
- MongoDB Data Modeling
- MongoDB Relational to Document Model Skill Badge
The social media project that uses the concepts shown above (the full source code for this tutorial)
Video demo:
Hope this tutorial helps you understand the basics about MongoDB with a social media application case study. Happy learning!