Advanced Application Architecture through Laravel's Service Container Management
Last updated on by Harris Raftopoulos
Laravel's service container serves as the foundation for sophisticated dependency management, enabling developers to build flexible, testable applications through powerful inversion of control patterns. This comprehensive system facilitates seamless class resolution and dependency injection across complex application architectures.
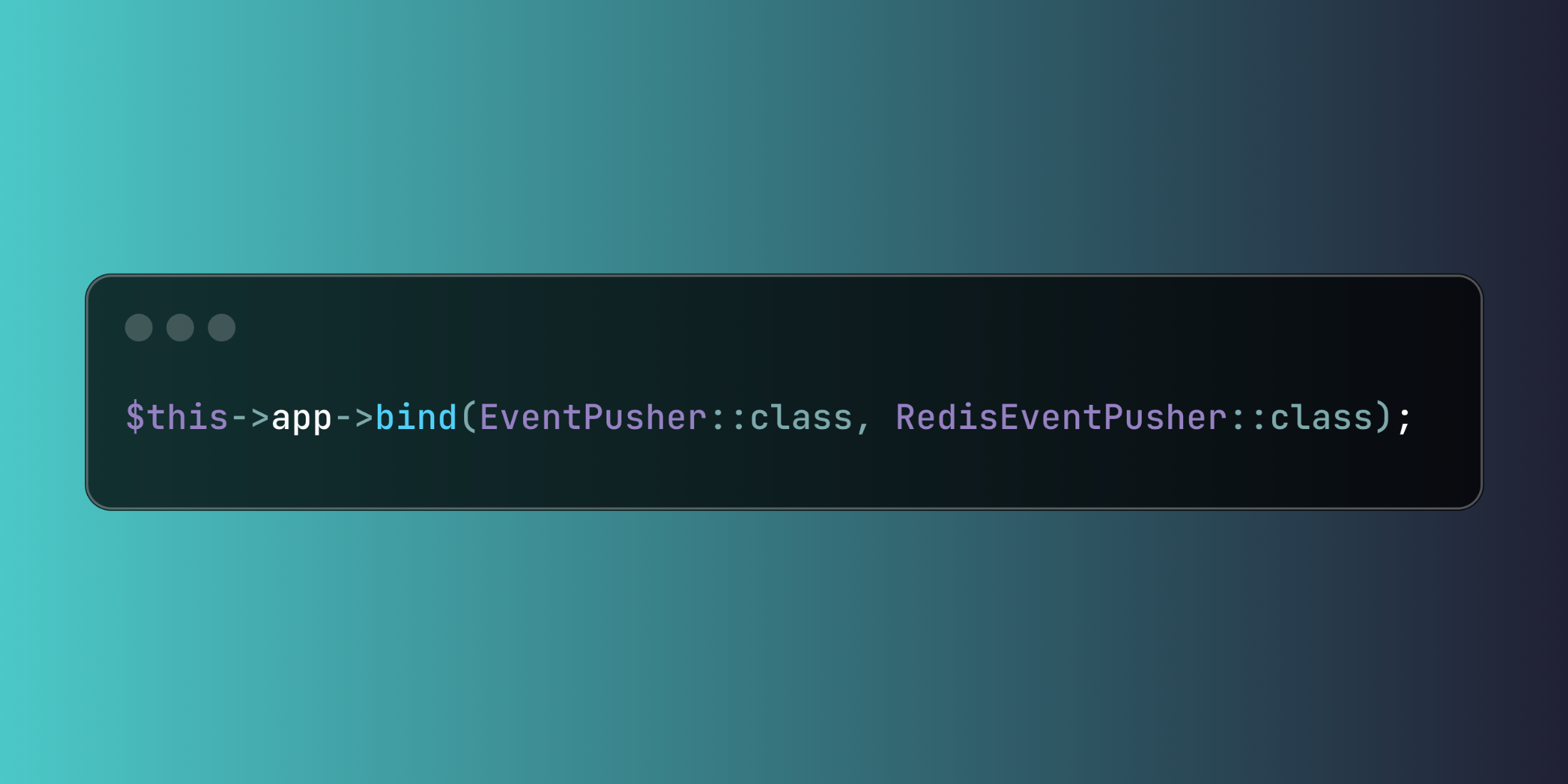
Interface-to-implementation bindings establish the fundamental container relationships:
use App\Contracts\EventPusher;use App\Services\RedisEventPusher; $this->app->bind(EventPusher::class, RedisEventPusher::class);Container resolution operates through multiple approaches, from automatic injection to explicit resolution:
$eventPusher = app(EventPusher::class);$eventPusher = $this->app->make(EventPusher::class); public function __construct(EventPusher $pusher){ $this->pusher = $pusher;}Singleton patterns ensure consistent instance management across application lifecycles:
$this->app->singleton(EventPusher::class, RedisEventPusher::class);Building a comprehensive notification system demonstrates advanced container capabilities across different service configurations:
interface NotificationService{ public function send($message, $recipient);} class EmailNotificationService implements NotificationService{ public function send($message, $recipient) { /* Implementation */ }} class SlackNotificationService implements NotificationService{ public function send($message, $recipient) { /* Implementation */ }} class AppServiceProvider extends ServiceProvider{ public function register() { $this->app->when(AdminController::class) ->needs(NotificationService::class) ->give(EmailNotificationService::class); $this->app->when(DeveloperController::class) ->needs(NotificationService::class) ->give(SlackNotificationService::class); $this->app->when(EmailNotificationService::class) ->needs('$apiKey') ->giveConfig('mail.api_key'); $this->app->bind(CpuReport::class, function () { return new CpuReport(); }); $this->app->bind(MemoryReport::class, function () { return new MemoryReport(); }); $this->app->tag([CpuReport::class, MemoryReport::class], 'reports'); }} class SystemMonitor{ public function __construct(iterable $reports) { $this->reports = $reports; }} $this->app->when(SystemMonitor::class) ->needs('$reports') ->giveTagged('reports');The container architecture supports extension patterns for service decoration, contextual binding for environment-specific implementations, and primitive value injection for configuration management. These capabilities enable sophisticated application designs while maintaining clean separation of concerns and comprehensive testability.