Laravel's string encryption capabilities now integrate directly into fluent chains, eliminating the need for cumbersome workarounds. The dedicated encrypt() and decrypt() methods maintain code readability while providing robust security features.
Traditional encryption workflows required breaking fluent chains or using awkward pipe methods:
$secureData = str('confidential-information') ->pipe(fn(Stringable $str) => encrypt($str->value())) ->upper() ->prepend('SEC_');The streamlined approach maintains natural flow throughout the entire operation:
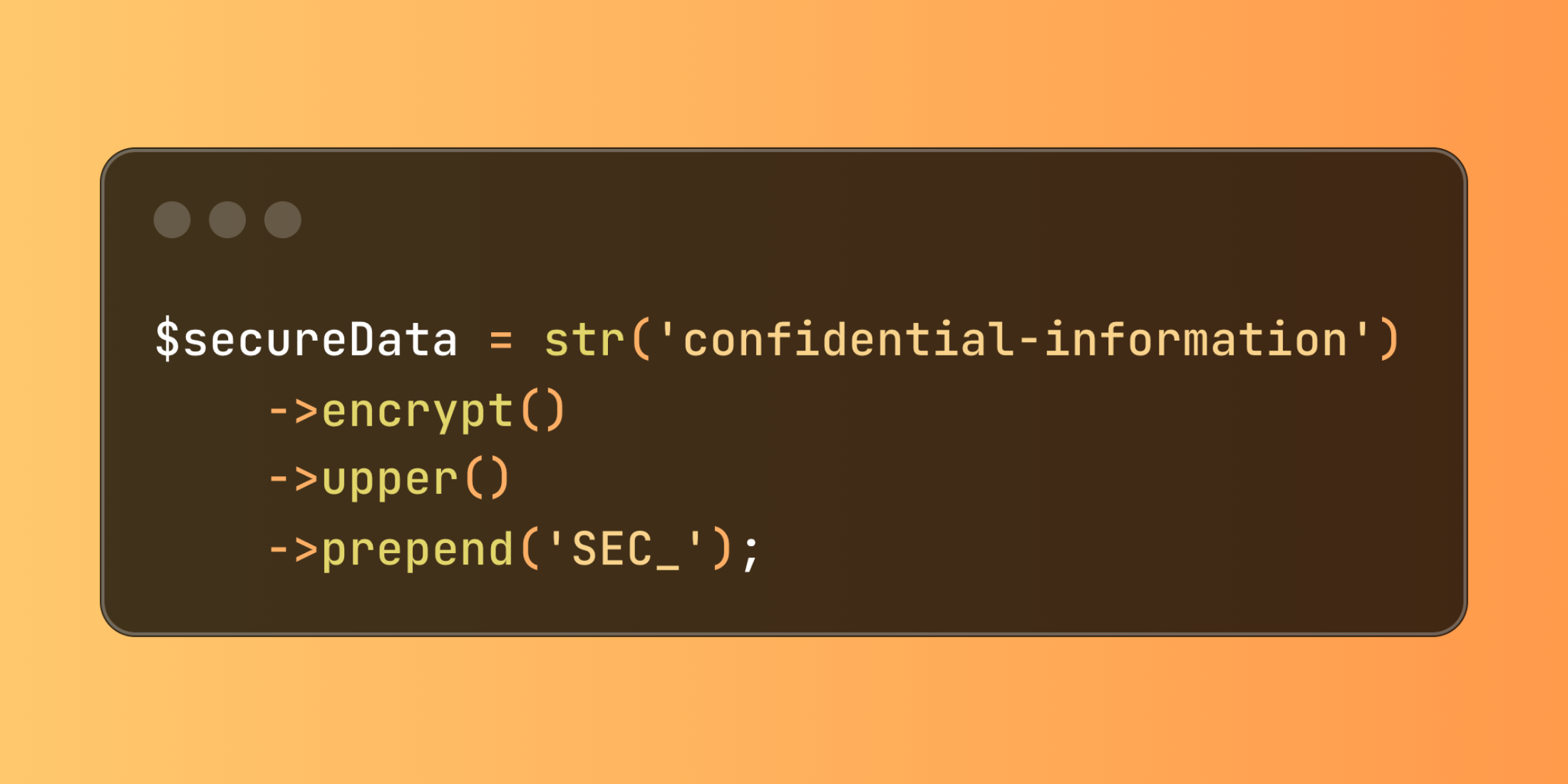
$secureData = str('confidential-information') ->encrypt() ->upper() ->prepend('SEC_');These methods integrate seamlessly with Laravel's existing encryption infrastructure, automatically utilizing your application's configured cipher and encryption key settings.
Consider a document management system requiring secure file identifiers with specific formatting requirements:
class DocumentSecurityManager{ public function createSecureIdentifier(string $documentId, string $department): string { return str($documentId) ->prepend($department . '_') ->append('_' . now()->timestamp) ->encrypt() ->prepend('DOC_') ->limit(64) ->toString(); } public function extractDocumentData(string $identifier): ?array { try { $decrypted = str($identifier) ->after('DOC_') ->decrypt() ->toString(); $parts = explode('_', $decrypted); return [ 'department' => $parts[0], 'document_id' => $parts[1], 'created_at' => $parts[2] ?? null, ]; } catch (Exception $e) { return null; } }} $manager = new DocumentSecurityManager();$identifier = $manager->createSecureIdentifier('report_2024', 'finance'); $data = $manager->extractDocumentData($identifier);This pattern excels when processing sensitive configuration data, user session tokens, or any scenario requiring encryption alongside string formatting operations. The fluent design eliminates intermediate variables while maintaining clear transformation steps throughout the entire pipeline.