Laravel's session blocking prevents race conditions and data inconsistencies by controlling concurrent session access. This feature ensures data integrity during simultaneous operations.
Understanding Session Blocking
Session blocking requires:
- Cache driver supporting atomic locks (redis, memcached, dynamodb, database)
- Non-cookie session driver
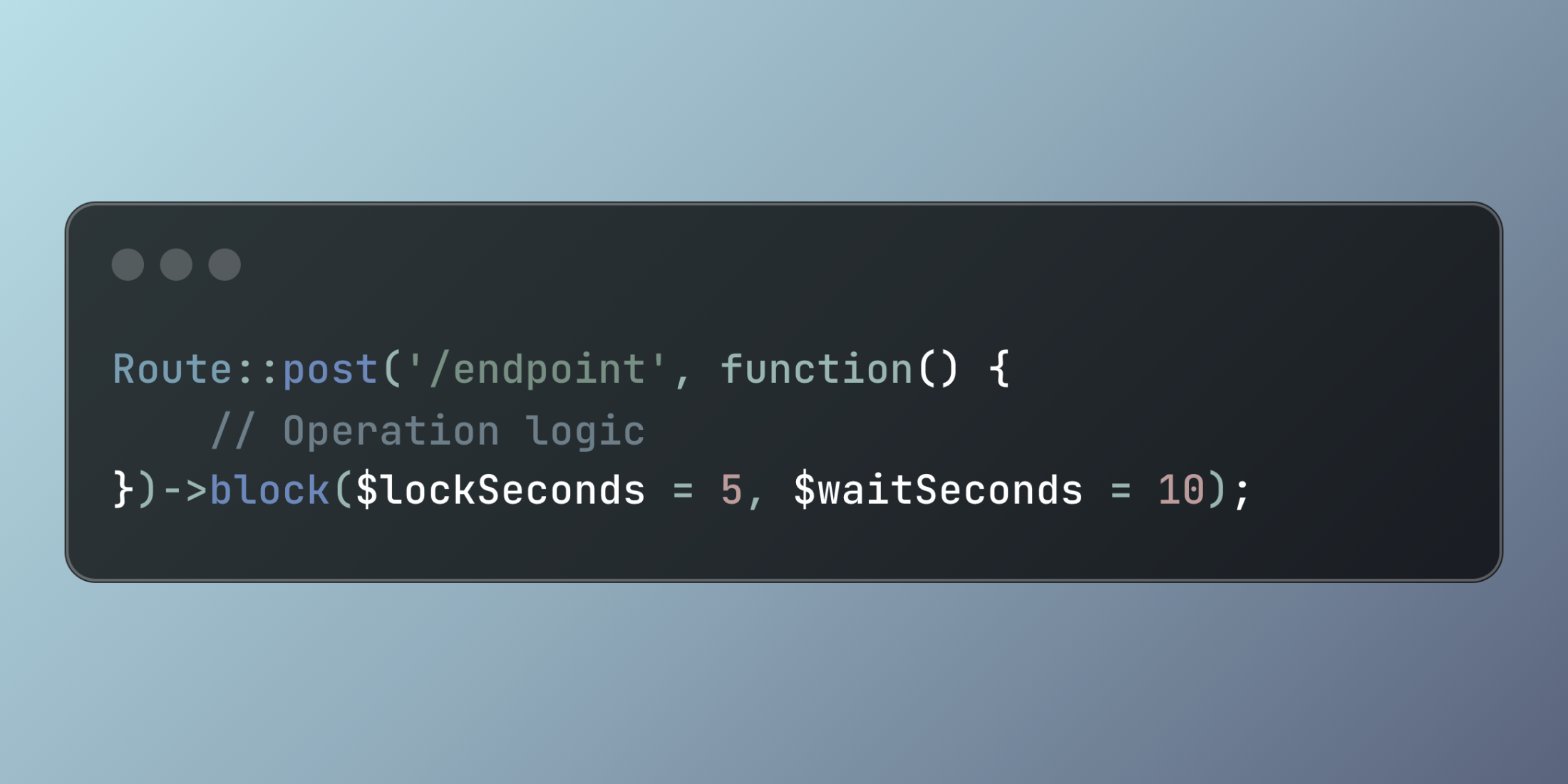
Route::post('/endpoint', function() { // Operation logic})->block($lockSeconds = 5, $waitSeconds = 10);Real-World Implementation
Let's build a payment processing system with concurrency control:
<?php namespace App\Http\Controllers; use App\Models\Payment;use Illuminate\Support\Facades\DB;use App\Exceptions\PaymentException; class PaymentController extends Controller{ public function process(Request $request) { return DB::transaction(function() use ($request) { // Validate payment exists and isn't processed $payment = Payment::findOrFail($request->payment_id); if ($payment->isProcessed()) { throw new PaymentException('Payment already processed'); } // Process payment $result = $this->paymentGateway->charge([ 'amount' => $payment->amount, 'currency' => $payment->currency, 'token' => $request->payment_token ]); $payment->markAsProcessed($result->transaction_id); return response()->json([ 'status' => 'success', 'transaction_id' => $result->transaction_id ]); }); }} // routes/api.phpRoute::post('/payments/process', [PaymentController::class, 'process'])->block(5, 10);This implementation:
- Prevents duplicate payment processing
- Waits up to 10 seconds for lock acquisition
- Uses database transactions for atomicity
- Handles concurrent requests gracefully
Session blocking provides a robust solution for managing concurrent requests, ensuring data integrity in high-traffic applications while maintaining a clean, Laravel-centric implementation.